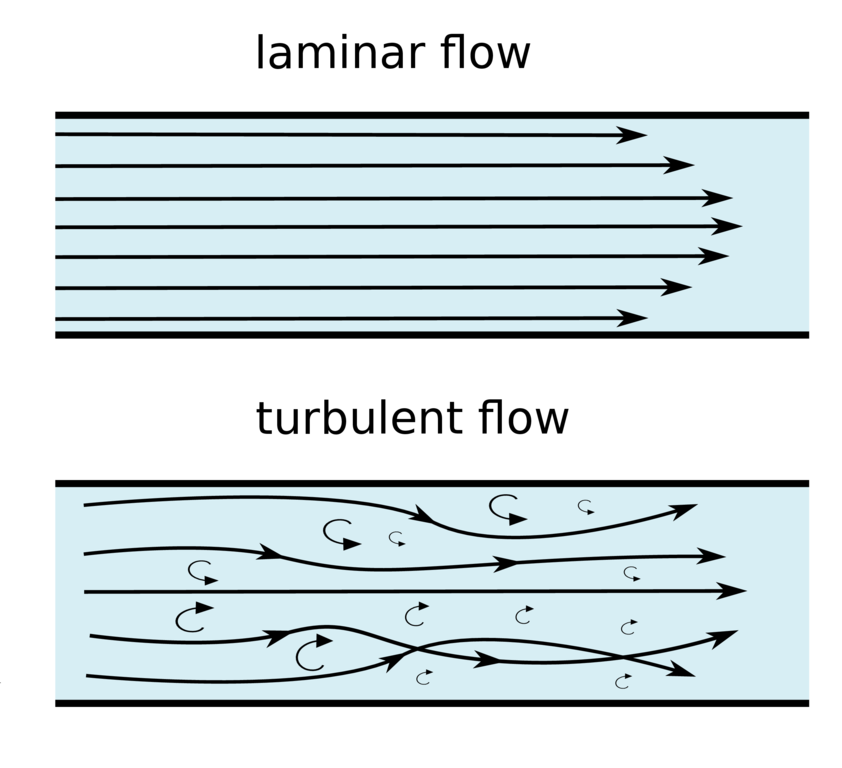
what is laminar flow and turbulent flow
These terms are descriptive of the flow because in laminar flow 1 layers of water flowing over one another at. Laminar flow is also referred to as streamline or viscous flow.

Laminar Flow Vs Turbulent Flow What Is Laminar Flow
A laminar stream is the development of liquid particles along with distinct ways or streamlines where all the streamlines out are straight and parallel.
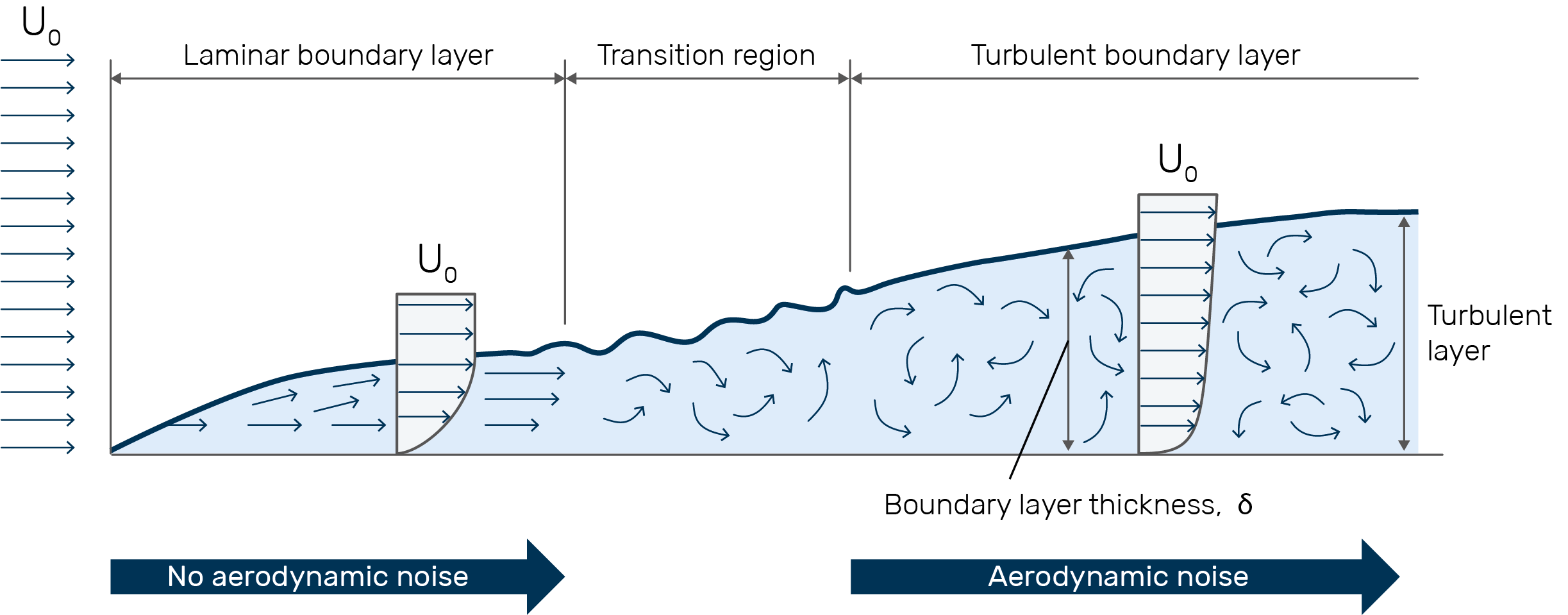
. If the fluid flow is highly ordered and smooth these fluid flows are called laminar flows. A turbulent boundary layer is more resistant to separation owing to the high energy within the BL compared to the laminar one. Turbulent flow occurs at high Reynolds.
What causes laminar and turbulent flow. Laminar Flow The steady flow of liquid over a horizontal surface in the form of layers of different velocities is called laminar flow. So in general a turbulent boundary layer is better to delay.
Re 2000 low velocity. Fluid particles move in straight lines. Laminar flows are smooth and streamlined whereas turbulent flows are irregular and chaotic.
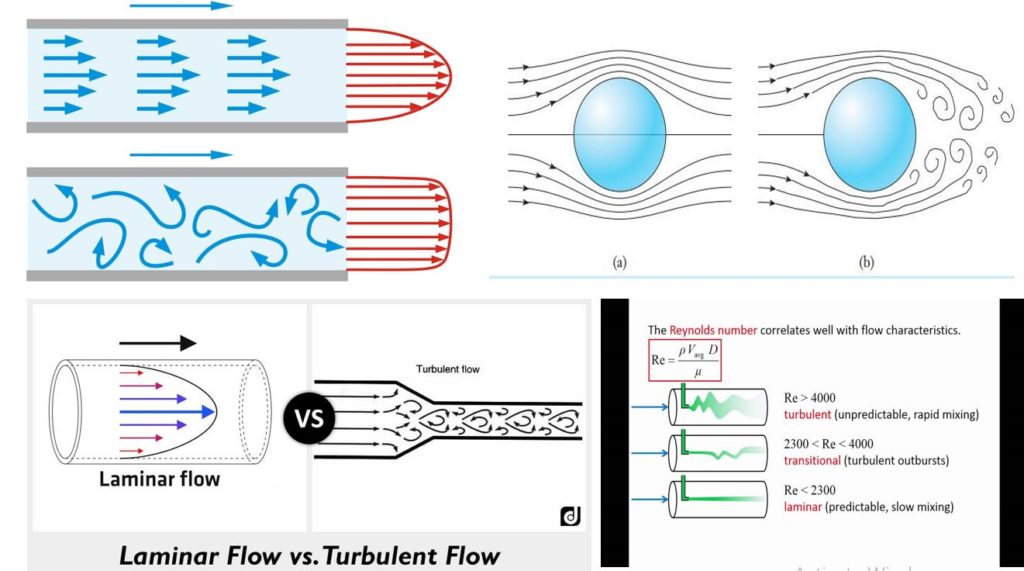
If Re is greater than 4000 the flow is turbulent. When a fluid is flowing through a closed channel such as a pipe or between two flat plates either of two types of flow may occur. Laminar flow definition is the straight quiet flow of water without any visible physical barriers.
Each of these flows behave in different manners in. In fluid dynamics turbulent flow is a type of flow in which fluid moves randomly in irregular or zigzag manner. The main difference between laminar and turbulent flows is the chaoticity of the flow.
Laminar flow is most often found at the front of a. If Re is less than 2000 the flow is laminar. The fluid layer crosses each other and does not move parallel.
What is laminar flow Class 11. This includes rapid variation of pressure and flow velocity in space and time. A low Reynolds number indicates laminar flow while a high Reynolds number indicates turbulent.
Transitional flow is a mixture of laminar and turbulent flow with turbulence in the center of the pipe and laminar flow near the edges. Subsequently the particles move in. Layers of water flow over one another at different speeds with virtually no mixing.
μ is the absolute viscosity of the fluid. Osborne Reynolds suggested that the nature of the flow of a fluid depends on its density flow rate the dimensions of the container through which it is flowing and its viscosity. Turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic property changes.
In contrast to laminar flow the fluid. Fluid layers do not cross each other and move parallel. Hence the particles move in.
Laminar flow is the movement of fluid particles along well-defined paths or streamlines where all the streamlines are straight and parallel. Laminar flow is caused by viscosity differences between the fluid and its surrounding environment. Laminar flow occurs at low Reynolds numbers where viscous forces are dominant and it is characterized by smooth constant fluid motion.
Laminar Flow is the smooth uninterrupted flow of air over the contour of the wings fuselage or other parts of an aircraft in flight. Turbulent flow is turbulent and chaotic in nature the flow is. It means that the water particles flow in parallel layers without physiological.
The fluid in a laminar flow environment moves at a constant speed and does not. Differences between Laminar and Turbulent flow-. Turbulent flow can characterize how fluid is moving with a laminar flow being a more smooth orderly flow and a turbulent flow being rough and chaotic.
ρ is the fluid density and.

1 Transition From Laminar Flow To Turbulent Flow As A Function Of Download Scientific Diagram
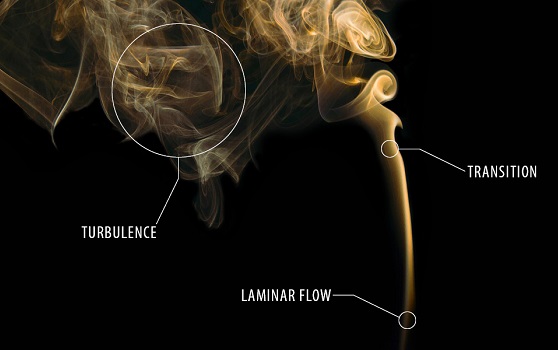
Flow Meters Laminar Flow Vs Turbulent Flow Bronkhorst

Airflow In Your Laboratory Laminar Flow Vs Turbulent Flow Air Science

Laminar Flow And Turbulent Flow The Constructor

Characteristics Of Laminar Flow Turbulent Flow Ibidi
File Laminar Vs Turbulent Flow 1 1024x571 Jpg Ccitonlinewiki
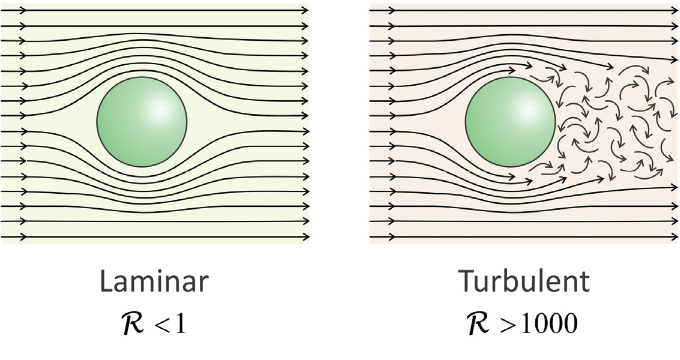
14 3 Laminar And Turbulent Flow Chemistry Libretexts

Laminar Flow Engineeringclicks
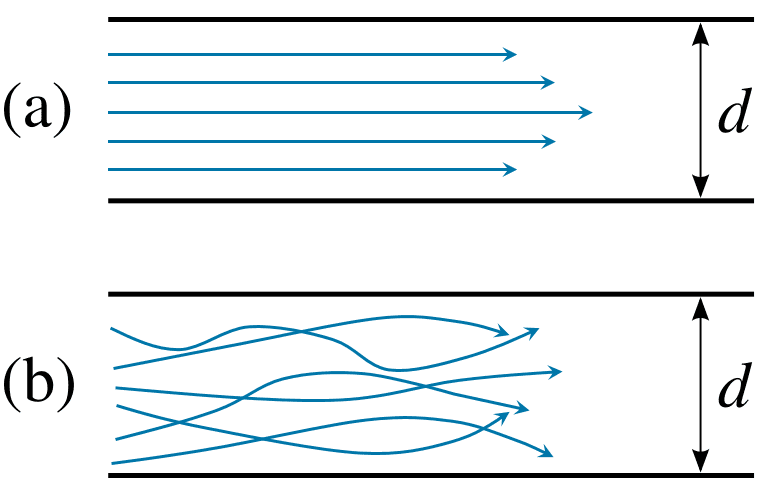
What Is Laminar Flow Computational Fluid Dynamics Simscale

Differentiate Laminar And Turbulent Flow M2 04 Fluid Mechanics In Tamil Youtube
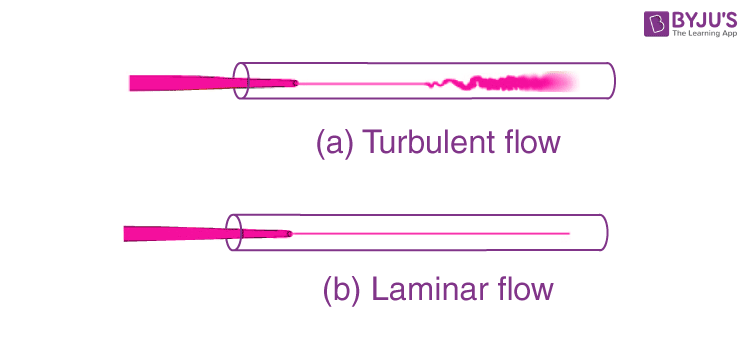
Streamline Flow Laminar Flow And Turbulent Flow Physics Byju S
Useful Information On Pipe Velocity

Flow Meters Laminar Flow Vs Turbulent Flow Bronkhorst

Aerodynamic Measurements Boundary Layer Components Gras

Solution Physics Laminar Flow Turbulent Flow Comparison Notes Studypool

Laminar Vs Turbulent Pressure Flow Rate Relations Mcgill 2011 Under Download Scientific Diagram

Laminar Vs Turbulent Flow Science Trends
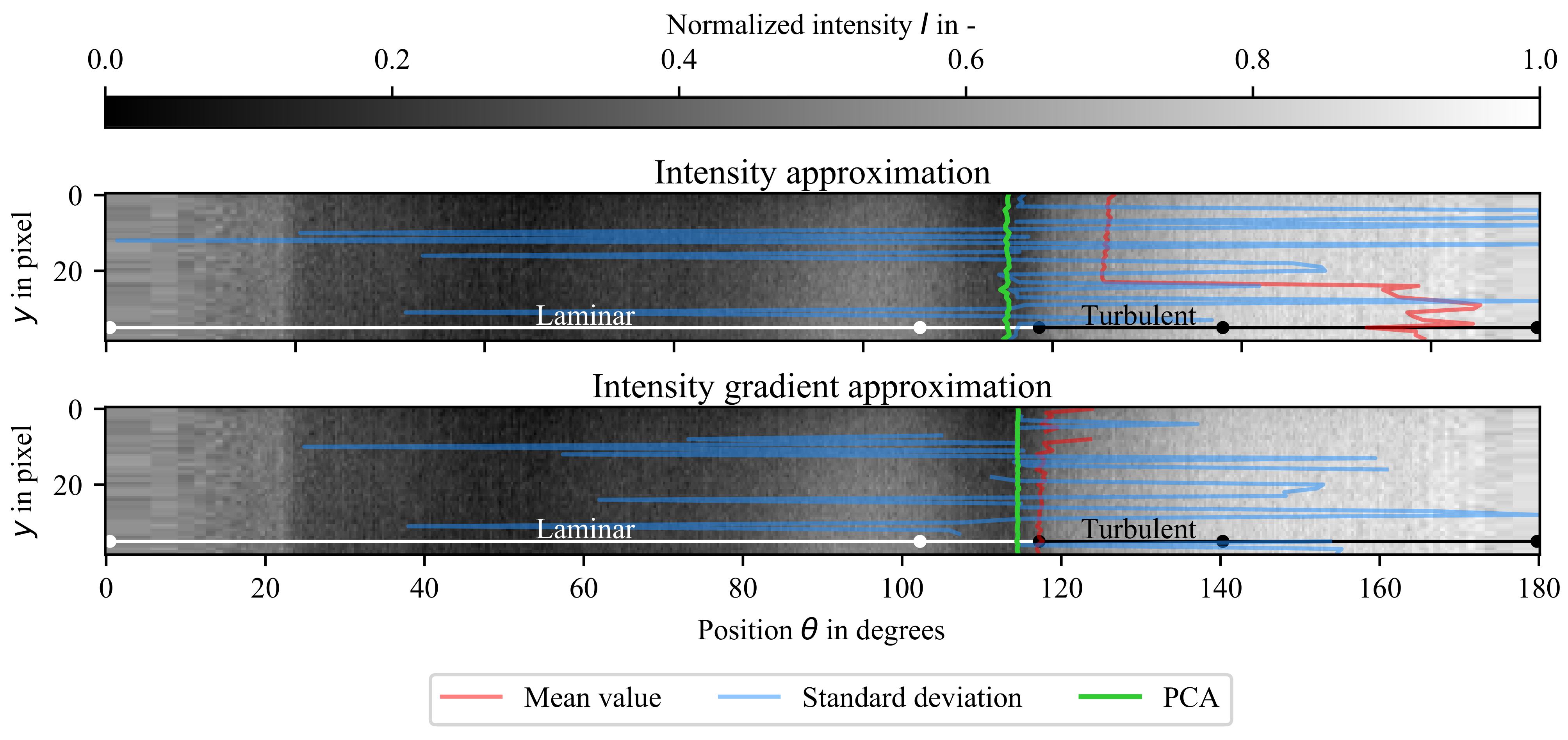
Applied Sciences Free Full Text Laminar Turbulent Transition Localization In Thermographic Flow Visualization By Means Of Principal Component Analysis Html